Discovery and Metadata
Drivers the system can access are represented by database entries. To simplify the creation of these entries available drivers can be scanned for and made available as a searchable list.
You can click scan from the Backoffice UI:
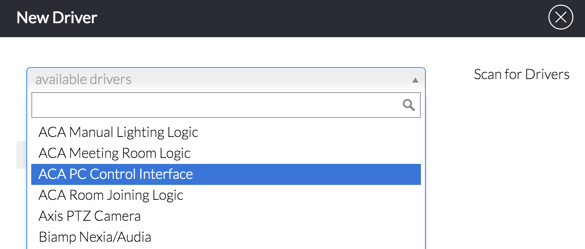
Metadata used to describe the drivers, is defined as part of the driver. For Example:
The discovery methods are made available to the driver by the line include ::Orchestrator::Constants. Without any discovery methods the driver is listed by its class name.
Discovery Methods
Method
Arguments
Description
descriptive_name
String
Used to describe the driver. This is what will be displayed in backoffice
generic_name
Symbol
The default generic name value
implements
Symbol
Defines the driver type, one of :ssh, :device, :service or :logic
description
String
A default description for the driver, supports markdown formatting
default_settings
Hash
Default settings that will be saved as JSON
tcp_port
Integer
Sets the default port and calls implements :device or implements :ssh if the port is 22
udp_port
Integer
Sets the default port and calls implements :device
uri_base
String
Expects a URI origin, such as http://overclockers.com.au:8080 and calls implements :service
makebreak!
Indicates that the TCP connection should not be held open
Last updated